
SL Paper 2
A student determined the percentage of the active ingredient magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2, in a 1.24 g antacid tablet.
The antacid tablet was added to 50.00 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 sulfuric acid, which was in excess.
Calculate the amount, in mol, of H2SO4.
Formulate the equation for the reaction of H2SO4 with Mg(OH)2.
The excess sulfuric acid required 20.80 cm3 of 0.1133 mol dm−3 NaOH for neutralization.
Calculate the amount of excess acid present.
Calculate the amount of H2SO4 that reacted with Mg(OH)2.
Determine the mass of Mg(OH)2 in the antacid tablet.
Calculate the percentage by mass of magnesium hydroxide in the 1.24 g antacid tablet to three significant figures.
Phosphoric acid, H3PO4, can undergo stepwise neutralization, forming amphiprotic species.
Formulate an equation for the reaction of one mole of phosphoric acid with one mole of sodium hydroxide.
Formulate two equations to show the amphiprotic nature of H2PO4−.
Calculate the concentration of H3PO4 if 25.00 cm3 is completely neutralised by the addition of 28.40 cm3 of 0.5000 mol dm−3 NaOH.
Outline the reason that sodium hydroxide is considered a Brønsted–Lowry base.
Iron may be extracted from iron (II) sulfide, FeS.
Iron (II) sulfide, FeS, is ionically bonded.
The first step in the extraction of iron from iron (II) sulfide is to roast it in air to form iron (III) oxide and sulfur dioxide.
Outline why metals, like iron, can conduct electricity.
Justify why sulfur is classified as a non-metal by giving two of its chemical properties.
Describe the bonding in this type of solid.
State the full electron configuration of the sulfide ion.
Outline, in terms of their electronic structures, why the ionic radius of the sulfide ion is greater than that of the oxide ion.
Suggest why chemists find it convenient to classify bonding into ionic, covalent and metallic.
Write the equation for this reaction.
Deduce the change in the oxidation state of sulfur.
Suggest why this process might raise environmental concerns.
Explain why the addition of small amounts of carbon to iron makes the metal harder.
Urea, (H2N)2CO, is excreted by mammals and can be used as a fertilizer.
Calculate the percentage by mass of nitrogen in urea to two decimal places using section 6 of the data booklet.
Suggest how the percentage of nitrogen affects the cost of transport of fertilizers giving a reason.
The structural formula of urea is shown.
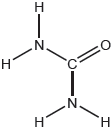
Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying the VSEPR theory.
Urea can be made by reacting potassium cyanate, KNCO, with ammonium chloride, NH4Cl.
KNCO(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) → (H2N)2CO(aq) + KCl(aq)
Determine the maximum mass of urea that could be formed from 50.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 potassium cyanate solution.
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH3(g) + CO2(g) (H2N)2CO(g) + H2O(g) ΔH < 0
Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc, when the temperature is increased.
Suggest one reason why urea is a solid and ammonia a gas at room temperature.
Sketch two different hydrogen bonding interactions between ammonia and water.
The combustion of urea produces water, carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
Formulate a balanced equation for the reaction.
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.
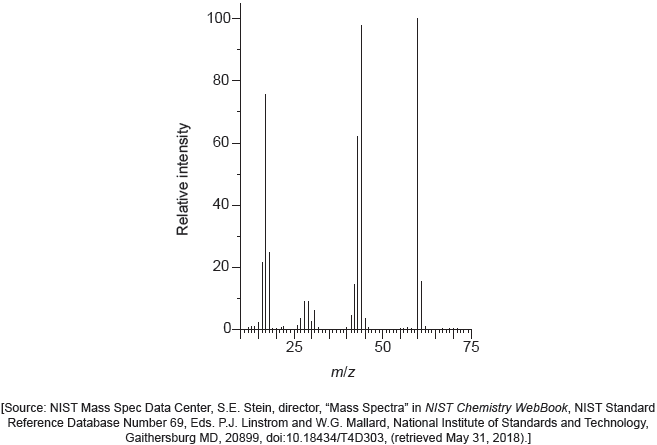
Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.
The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.
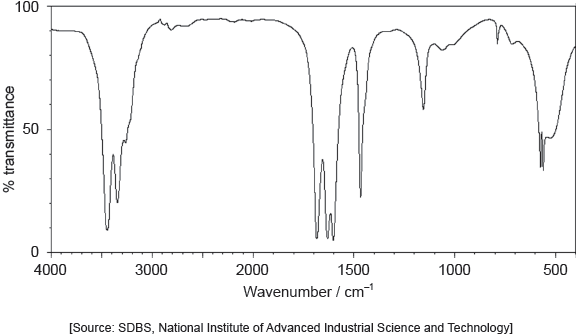
Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.
Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
Menthol is an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Complete combustion of 0.1595 g of menthol produces 0.4490 g of carbon dioxide and 0.1840 g of water. Determine the empirical formula of the compound showing your working.
0.150 g sample of menthol, when vaporized, had a volume of 0.0337 dm3 at 150 °C and 100.2 kPa. Calculate its molar mass showing your working.
Automobile air bags inflate by a rapid decomposition reaction. One typical compound used is guanidinium nitrate, C(NH2)3NO3, which decomposes very rapidly to form nitrogen, water vapour and carbon.
Deduce the equation for the decomposition of guanidinium nitrate.
Calculate the total number of moles of gas produced from the decomposition of 10.0 g of guanidinium nitrate.
Calculate the pressure, in kPa, of this gas in a 10.0 dm3 air bag at 127°C, assuming no gas escapes.
Suggest why water vapour deviates significantly from ideal behaviour when the gases are cooled, while nitrogen does not.
Another airbag reactant produces nitrogen gas and sodium.
Suggest, including an equation, why the products of this reactant present a safety hazard.
Propan-2-ol is a useful organic solvent.
Draw the structural formula of propan-2-ol.
Calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in 1.00 g of propan-2-ol.
Classify propan-2-ol as a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol, giving a reason.
State a suitable oxidizing agent for the oxidation of propan-2-ol in an acidified aqueous solution.
Deduce the average oxidation state of carbon in propan-2-ol.
Deduce the product of the oxidation of propan-2-ol with the oxidizing agent in (d)(i).
When heated in air, magnesium ribbon reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
The reaction in (a)(i) was carried out in a crucible with a lid and the following data was recorded:
Mass of crucible and lid = 47.372 ±0.001 g
Mass of crucible, lid and magnesium ribbon before heating = 53.726 ±0.001 g
Mass of crucible, lid and product after heating = 56.941 ±0.001 g
When magnesium is burnt in air, some of it reacts with nitrogen to form magnesium nitride according to the equation:
3 Mg (s) + N2 (g) → Mg3N2 (s)
The presence of magnesium nitride can be demonstrated by adding water to the product. It is hydrolysed to form magnesium hydroxide and ammonia.
Most nitride ions are 14N3–.
Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs.
State the block of the periodic table in which magnesium is located.
Identify a metal, in the same period as magnesium, that does not form a basic oxide.
Calculate the amount of magnesium, in mol, that was used.
Determine the percentage uncertainty of the mass of product after heating.
Assume the reaction in (a)(i) is the only one occurring and it goes to completion, but some product has been lost from the crucible. Deduce the percentage yield of magnesium oxide in the crucible.
Evaluate whether this, rather than the loss of product, could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
Suggest an explanation, other than product being lost from the crucible or reacting with nitrogen, that could explain the yield found in (b)(iii).
Calculate coefficients that balance the equation for the following reaction.
__ Mg3N2 (s) + __ H2O (l) → __ Mg(OH)2 (s) + __ NH3 (aq)
Determine the oxidation state of nitrogen in Mg3N2 and in NH3.
Deduce, giving reasons, whether the reaction of magnesium nitride with water is an acid–base reaction, a redox reaction, neither or both.
State the number of subatomic particles in this ion.
Some nitride ions are 15N3–. State the term that describes the relationship between 14N3– and 15N3–.
The nitride ion and the magnesium ion are isoelectronic (they have the same electron configuration). Determine, giving a reason, which has the greater ionic radius.
Suggest two reasons why atoms are no longer regarded as the indivisible units of matter.
State the types of bonding in magnesium, oxygen and magnesium oxide, and how the valence electrons produce these types of bonding.
Magnesium is a group 2 metal which exists as a number of isotopes and forms many compounds.
State the nuclear symbol notation, , for magnesium-26.
Mass spectroscopic analysis of a sample of magnesium gave the following results:
Calculate the relative atomic mass, Ar, of this sample of magnesium to two decimal places.
Magnesium burns in air to form a white compound, magnesium oxide. Formulate an equation for the reaction of magnesium oxide with water.
Describe the trend in acid-base properties of the oxides of period 3, sodium to chlorine.
In addition to magnesium oxide, magnesium forms another compound when burned in air. Suggest the formula of this compound
Describe the structure and bonding in solid magnesium oxide.
Magnesium chloride can be electrolysed.
Deduce the half-equations for the reactions at each electrode when molten magnesium chloride is electrolysed, showing the state symbols of the products. The melting points of magnesium and magnesium chloride are 922 K and 987 K respectively.
Anode (positive electrode):
Cathode (negative electrode):
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) can be determined by the Winkler Method.
A 25.00 cm3 sample of water was treated according to the Winkler Method.
Step I: 2Mn2+ (aq) + O2 (g) + 4OH− (aq) → 2MnO2 (s) + 2H2O (l)
Step II: MnO2 (s) + 2I− (aq) + 4H+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq) + I2 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
Step III: 2S2O32− (aq) + I2 (aq) → 2I− (aq) + S4O62− (aq)
The iodine produced was titrated with 37.50 cm3 of 5.000 × 10−4 mol dm−3 Na2S2O3.
Outline what is measured by BOD.
A student dissolved 0.1240 ± 0.0001 g of Na2S2O3 to make 1000.0 ± 0.4 cm3 of solution to use in the Winkler Method.
Determine the percentage uncertainty in the molar concentration.
Calculate the amount, in moles of Na2S2O3 used in the titration.
Deduce the mole ratio of O2 consumed in step I to S2O32− used in step III.
Calculate the concentration of dissolved oxygen, in mol dm−3, in the sample.
The three steps of the Winkler Method are redox reactions.
Deduce the reduction half-equation for step II.
The following shows some compounds which can be made from ethene, C2H4.
ethene (C2H4) → C2H5Cl → C2H6O → C2H4O
State the type of reaction which converts ethene into C2H5Cl.
Write an equation for the reaction of C2H5Cl with aqueous sodium hydroxide to produce a C2H6O compound, showing structural formulas.
Write an equation for the complete combustion of the organic product in (b).
Determine the enthalpy of combustion of the organic product in (b), in kJ mol−1, using data from section 11 of the data booklet.
State the reagents and conditions for the conversion of the compound C2H6O, produced in (b), into C2H4O.
Explain why the compound C2H6O, produced in (b), has a higher boiling point than compound C2H4O, produced in d(i).
Ethene is often polymerized. Draw a section of the resulting polymer, showing two repeating units.
This question is about compounds of sodium.
Sodium peroxide is used in diving apparatus to produce oxygen from carbon dioxide.
2Na2O2 (s) + 2CO2 (g) → 2Na2CO3 (s) + O2 (g)
Describe the structure and bonding in solid sodium oxide.
Write equations for the separate reactions of solid sodium oxide and solid phosphorus(V) oxide with excess water and differentiate between the solutions formed.
Sodium oxide, Na2O:
Phosphorus(V) oxide, P4O10:
Differentiation:
Sodium peroxide, Na2O2, is formed by the reaction of sodium oxide with oxygen.
2Na2O (s) + O2 (g) → 2Na2O2 (s)
Calculate the percentage yield of sodium peroxide if 5.00 g of sodium oxide produces 5.50 g of sodium peroxide.
Determine the enthalpy change, ΔH, in kJ, for this reaction using data from the table and section 12 of the data booklet.
Outline why bond enthalpy values are not valid in calculations such as that in (c)(i).
The reaction of sodium peroxide with excess water produces hydrogen peroxide and one other sodium compound. Suggest the formula of this compound.
State the oxidation number of carbon in sodium carbonate, Na2CO3.
3.26 g of iron powder are added to 80.0 cm3 of 0.200 mol dm−3 copper(II) sulfate solution. The following reaction occurs:
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Determine the limiting reactant showing your working.
The mass of copper obtained experimentally was 0.872 g. Calculate the percentage yield of copper.
The reaction was carried out in a calorimeter. The maximum temperature rise of the solution was 7.5 °C.
Calculate the enthalpy change, ΔH, of the reaction, in kJ, assuming that all the heat released was absorbed by the solution. Use sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
State another assumption you made in (b)(i).
The only significant uncertainty is in the temperature measurement.
Determine the absolute uncertainty in the calculated value of ΔH if the uncertainty in the temperature rise was ±0.2 °C.
Sketch a graph of the concentration of iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4, against time as the reaction proceeds.
Outline how the initial rate of reaction can be determined from the graph in part (c)(i).
Explain, using the collision theory, why replacing the iron powder with a piece of iron of the same mass slows down the rate of the reaction.
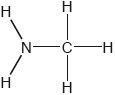
Two hydrides of nitrogen are ammonia and hydrazine, N2H4. One derivative of ammonia is methanamine whose molecular structure is shown below.
Hydrazine is used to remove oxygen from water used to generate steam or hot water.
N2H4(aq) + O2(aq) → N2(g) + 2H2O(l)
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in a sample of water is 8.0 × 10−3 gdm−3.
Estimate the H−N−H bond angle in methanamine using VSEPR theory.
Ammonia reacts reversibly with water.
NH3(g) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH−(aq)
Explain the effect of adding H+(aq) ions on the position of the equilibrium.
Hydrazine reacts with water in a similar way to ammonia. Deduce an equation for the reaction of hydrazine with water.
Outline, using an ionic equation, what is observed when magnesium powder is added to a solution of ammonium chloride.
Hydrazine has been used as a rocket fuel. The propulsion reaction occurs in several stages but the overall reaction is:
N2H4(l) → N2(g) + 2H2(g)
Suggest why this fuel is suitable for use at high altitudes.
Determine the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔH, in kJ, when 1.00 mol of gaseous hydrazine decomposes to its elements. Use bond enthalpy values in section 11 of the data booklet.
N2H4(g) → N2(g) + 2H2(g)
The standard enthalpy of formation of N2H4(l) is +50.6 kJmol−1. Calculate the enthalpy of vaporization, ΔHvap, of hydrazine in kJmol−1.
N2H4(l) → N2H4(g)
(If you did not get an answer to (f), use −85 kJ but this is not the correct answer.)
Calculate, showing your working, the mass of hydrazine needed to remove all the dissolved oxygen from 1000 dm3 of the sample.
Calculate the volume, in dm3, of nitrogen formed under SATP conditions. (The volume of 1 mol of gas = 24.8 dm3 at SATP.)
Sodium thiosulfate solution reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form a precipitate of sulfur at room temperature.
Na2S2O3 (aq) + 2HCl (aq) → S (s) + SO2 (g) + 2NaCl (aq) + X
Identify the formula and state symbol of X.
Suggest why the experiment should be carried out in a fume hood or in a well-ventilated laboratory.
The precipitate of sulfur makes the mixture cloudy, so a mark underneath the reaction mixture becomes invisible with time.
10.0 cm3 of 2.00 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid was added to a 50.0 cm3 solution of sodium thiosulfate at temperature, T1. Students measured the time taken for the mark to be no longer visible to the naked eye. The experiment was repeated at different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate.
Show that the hydrochloric acid added to the flask in experiment 1 is in excess.
Draw the best fit line of against concentration of sodium thiosulfate on the axes provided.
A student decided to carry out another experiment using 0.075 mol dm-3 solution of sodium thiosulfate under the same conditions. Determine the time taken for the mark to be no longer visible.
An additional experiment was carried out at a higher temperature, T2.
(i) On the same axes, sketch Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves at the two temperatures T1 and T2, where T2 > T1.
(ii) Explain why a higher temperature causes the rate of reaction to increase.
Suggest one reason why the values of rates of reactions obtained at higher temperatures may be less accurate.
Magnetite, Fe3O4, is another ore of iron that contains both Fe2+ and Fe3+.
Iron exists as several isotopes.
In acidic solution, hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, will oxidize Fe2+.
Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e−
Deduce the ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+ in Fe3O4.
State the type of spectroscopy that could be used to determine their relative abundances.
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in each species.
Iron has a relatively small specific heat capacity; the temperature of a 50 g sample rises by 44.4°C when it absorbs 1 kJ of heat energy.
Determine the specific heat capacity of iron, in J g−1 K−1. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
Write the half-equation for the reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water in acidic solution.
Deduce a balanced equation for the oxidation of Fe2+ by acidified hydrogen peroxide.
White phosphorus is an allotrope of phosphorus and exists as P4.
An equilibrium exists between PCl3 and PCl5.
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) PCl5 (g)
Sketch the Lewis (electron dot) structure of the P4 molecule, containing only single bonds.
Write an equation for the reaction of white phosphorus (P4) with chlorine gas to form phosphorus trichloride (PCl3).
Deduce the electron domain and molecular geometry using VSEPR theory, and estimate the Cl–P–Cl bond angle in PCl3.
Explain the polarity of PCl3.
Calculate the standard enthalpy change (ΔH⦵) for the forward reaction in kJ mol−1.
ΔH⦵f PCl3 (g) = −306.4 kJ mol−1
ΔH⦵f PCl5 (g) = −398.9 kJ mol−1
State the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for this reaction.
State, with a reason, the effect of an increase in temperature on the position of this equilibrium.
Titanium is a transition metal.
TiCl4 reacts with water and the resulting titanium(IV) oxide can be used as a smoke screen.
Describe the bonding in metals.
Titanium exists as several isotopes. The mass spectrum of a sample of titanium gave the following data:
Calculate the relative atomic mass of titanium to two decimal places.
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the atom.
State the full electron configuration of the 2+ ion.
Explain why an aluminium-titanium alloy is harder than pure aluminium.
State the type of bonding in potassium chloride which melts at 1043 K.
A chloride of titanium, TiCl4, melts at 248 K. Suggest why the melting point is so much lower than that of KCl.
Formulate an equation for this reaction.
Suggest one disadvantage of using this smoke in an enclosed space.
An acidic sample of a waste solution containing Sn2+(aq) reacted completely with K2Cr2O7 solution to form Sn4+(aq).
State the oxidation half-equation.
Deduce the overall redox equation for the reaction between acidic Sn2+(aq) and Cr2O72–(aq), using section 24 of the data booklet.
Calculate the percentage uncertainty for the mass of K2Cr2O7(s) from the given data.
The sample of K2Cr2O7(s) in (i) was dissolved in distilled water to form 0.100 dm3 solution. Calculate its molar concentration.
10.0 cm3 of the waste sample required 13.24 cm3 of the K2Cr2O7 solution. Calculate the molar concentration of Sn2+(aq) in the waste sample.
Chlorine undergoes many reactions.
of manganese(IV) oxide was added to of .
Chlorine gas reacts with water to produce hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid.
is a common chlorofluorocarbon, .
State the full electron configuration of the chlorine atom.
State, giving a reason, whether the chlorine atom or the chloride ion has a larger radius.
Outline why the chlorine atom has a smaller atomic radius than the sulfur atom.
The mass spectrum of chlorine is shown.
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2014 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved.
Outline the reason for the two peaks at and .
Explain the presence and relative abundance of the peak at .
Calculate the amount, in , of manganese(IV) oxide added.
Determine the limiting reactant, showing your calculations.
Determine the excess amount, in , of the other reactant.
Calculate the volume of chlorine, in , produced if the reaction is conducted at standard temperature and pressure (STP). Use section 2 of the data booklet.
State the oxidation state of manganese in and .
Deduce, referring to oxidation states, whether is an oxidizing or reducing agent.
Hypochlorous acid is considered a weak acid. Outline what is meant by the term weak acid.
State the formula of the conjugate base of hypochlorous acid.
Calculate the concentration of in a solution with a .
State the type of reaction occurring when ethane reacts with chlorine to produce chloroethane.
Predict, giving a reason, whether ethane or chloroethane is more reactive.
Write the equation for the reaction of chloroethane with a dilute aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
Deduce the nucleophile for the reaction in d(iii).
Ethoxyethane (diethyl ether) can be used as a solvent for this conversion. Draw the structural formula of ethoxyethane
Deduce the number of signals and their chemical shifts in the spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
Calculate the percentage by mass of chlorine in .
Comment on how international cooperation has contributed to the lowering of emissions responsible for ozone depletion.
The biochemical oxygen demand of a water sample can be determined by the following series of reactions. The final step is titration of the sample with sodium thiosulfate solution, Na2S2O3 (aq).
2Mn2+ (aq) + O2 (aq) + 4OH− (aq) → 2MnO2 (s) + 2H2O (l)
MnO2 (s) + 2I− (aq) + 4H+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq) + I2 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
2S2O32− (aq) + I2 (aq) → 2I− (aq) + S4O62− (aq)
A student analysed two 300.0 cm3 samples of water taken from the school pond: one immediately (day 0), and the other after leaving it sealed in a dark cupboard for five days (day 5). The following results were obtained for the titration of the samples with 0.0100 mol dm−3 Na2S2O3 (aq).
Determine the mole ratio of S2O32− to O2, using the balanced equations.
Calculate the number of moles of oxygen in the day 0 sample.
The day 5 sample contained 5.03 × 10−5 moles of oxygen.
Determine the 5-day biochemical oxygen demand of the pond, in mg dm−3 (“parts per million”, ppm).
Calculate the percentage uncertainty of the day 5 titre.
Suggest a modification to the procedure that would make the results more reliable.
Lithium reacts with water to form an alkaline solution.
A 0.200 g piece of lithium was placed in 500.0 cm3 of water.
Determine the coefficients that balance the equation for the reaction of lithium with water.
Calculate the molar concentration of the resulting solution of lithium hydroxide.
Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas produced, in cm3, if the temperature was 22.5 °C and the pressure was 103 kPa. Use sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
Suggest a reason why the volume of hydrogen gas collected was smaller than predicted.
The reaction of lithium with water is a redox reaction. Identify the oxidizing agent in the reaction giving a reason.
Describe two observations that indicate the reaction of lithium with water is exothermic.
Hydrogen peroxide can react with methane and oxygen to form methanol. This reaction can occur below 50°C if a gold nanoparticle catalyst is used.
Methanol is usually manufactured from methane in a two-stage process.
CH4 (g) + H2O (g) CO (g) + 3H2 (g)
CO (g) + 2H2 (g) CH3OH (l)
Consider the first stage of the reaction.
CH4 (g) + H2O (g) CO (g) + 3H2 (g)
The diagram shows the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve for the uncatalyzed reaction.
Draw a distribution curve at a lower temperature (T2) and show on the diagram how the addition of a catalyst enables the reaction to take place more rapidly than at T1.
The hydrogen peroxide could cause further oxidation of the methanol. Suggest a possible oxidation product.
Determine the overall equation for the production of methanol.
8.00 g of methane is completely converted to methanol. Calculate, to three significant figures, the final volume of hydrogen at STP, in dm3. Use sections 2 and 6 of the data booklet.
Determine the enthalpy change, ΔH, in kJ. Use section 11 of the data booklet.
Bond enthalpy of CO = 1077 kJ mol−1.
State the expression for Kc for this stage of the reaction.
State and explain the effect of increasing temperature on the value of Kc.
The thermal decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide occurs according to the equation:
2N2O (g) → 2N2 (g) + O2 (g)
The reaction can be followed by measuring the change in total pressure, at constant temperature, with time.
The x-axis and y-axis are shown with arbitrary units.
Explain why, as the reaction proceeds, the pressure increases by the amount shown.
Outline, in terms of collision theory, how a decrease in pressure would affect the rate of reaction.
The experiment is repeated using the same amount of dinitrogen monoxide in the same apparatus, but at a lower temperature.
Sketch, on the axes in question 2, the graph that you would expect.
The experiment gave an error in the rate because the pressure gauge was inaccurate. Outline whether repeating the experiment, using the same apparatus, and averaging the results would reduce the error.
The graph below shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies at a particular temperature.
The rate at which dinitrogen monoxide decomposes is significantly increased by a metal oxide catalyst.
Annotate and use the graph to outline why a catalyst has this effect.
This reaction is used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g) Kc = 280 at 1000 K
State why this equilibrium reaction is considered homogeneous.
0.200 mol sulfur dioxide, 0.300 mol oxygen and 0.500 mol sulfur trioxide were mixed in a 1.00 dm3 flask at 1000 K.
Predict the direction of the reaction showing your working.
Limestone can be converted into a variety of useful commercial products through the lime cycle. Limestone contains high percentages of calcium carbonate, CaCO3.
The second step of the lime cycle produces calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2.
Calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide to reform calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
Calcium carbonate is heated to produce calcium oxide, CaO.
CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide produced at STP when 555 g of calcium carbonate decomposes. Use sections 2 and 6 of the data booklet.
Thermodynamic data for the decomposition of calcium carbonate is given.
Calculate the enthalpy change of reaction, ΔH, in kJ, for the decomposition of calcium carbonate.
The potential energy profile for a reaction is shown. Sketch a dotted line labelled “Catalysed” to indicate the effect of a catalyst.
Outline why a catalyst has such an effect.
Write the equation for the reaction of Ca(OH)2 (aq) with hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq).
Determine the volume, in dm3, of 0.015 mol dm−3 calcium hydroxide solution needed to neutralize 35.0 cm3 of 0.025 mol dm−3 HCl (aq).
Saturated calcium hydroxide solution is used to test for carbon dioxide. Calculate the pH of a 2.33 × 10−2 mol dm−3 solution of calcium hydroxide, a strong base.
Determine the mass, in g, of CaCO3 (s) produced by reacting 2.41 dm3 of 2.33 × 10−2 mol dm−3 of Ca(OH)2 (aq) with 0.750 dm3 of CO2 (g) at STP.
2.85 g of CaCO3 was collected in the experiment in e(i). Calculate the percentage yield of CaCO3.
(If you did not obtain an answer to e(i), use 4.00 g, but this is not the correct value.)
Outline how one calcium compound in the lime cycle can reduce a problem caused by acid deposition.
Iron (II) sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form hydrogen sulfide, H2S.
In aqueous solution, hydrogen sulfide acts as an acid.
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structure of hydrogen sulfide.
Predict the shape of the hydrogen sulfide molecule.
State the formula of its conjugate base.
Saturated aqueous hydrogen sulfide has a concentration of 0.10 mol dm−3 and a pH of 4.0. Demonstrate whether it is a strong or weak acid.
Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration in saturated aqueous hydrogen sulfide.
A gaseous sample of nitrogen, contaminated only with hydrogen sulfide, was reacted with excess sodium hydroxide solution at constant temperature. The volume of the gas changed from 550 cm3 to 525 cm3.
Determine the mole percentage of hydrogen sulfide in the sample, stating one assumption you made.
Benzoic acid, C6H5COOH, is another derivative of benzene.
Draw the structure of the conjugate base of benzoic acid showing all the atoms and all the bonds.
The pH of an aqueous solution of benzoic acid at 298 K is 2.95. Determine the concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution, using section 2 of the data booklet.
Formulate the equation for the complete combustion of benzoic acid in oxygen using only integer coefficients.
Suggest how benzoic acid, Mr = 122.13, forms an apparent dimer, Mr = 244.26, when dissolved in a non-polar solvent such as hexane.
A 4.406 g sample of a compound containing only C, H and O was burnt in excess oxygen. 8.802 g of CO2 and 3.604 g of H2O were produced.
The following spectrums show the Infrared spectra of propan-1-ol, propanal and propanoic acid.
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. All rights reserved. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C71238&Units=SI&Type=IRSPEC&Index=3#IR-SPEC [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C79094&Units=SI&Mask=80#IR-Spec [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.
NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=propanal&Units=SI&cIR=on&cTZ=on#IRSpec [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.
Determine the empirical formula of the compound using section 6 of the data booklet.
Determine the molecular formula of this compound if its molar mass is 88.12 g mol−1. If you did not obtain an answer in (a) use CS, but this is not the correct answer.
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.
Soluble acids and bases ionize in water.
Sodium hypochlorite ionizes in water.
OCl–(aq) + H2O(l) OH–(aq) + HOCl(aq)
A solution containing 0.510 g of an unknown monoprotic acid, HA, was titrated with 0.100 mol dm–3 NaOH(aq). 25.0 cm3 was required to reach the equivalence point.
Identify the amphiprotic species.
Identify one conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction.
Calculate the amount, in mol, of NaOH(aq) used.
Calculate the molar mass of the acid.
Calculate [H+] in the NaOH solution.
The concentration of a solution of a weak acid, such as ethanedioic acid, can be determined
by titration with a standard solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq).
Distinguish between a weak acid and a strong acid.
Weak acid:
Strong acid:
Suggest why it is more convenient to express acidity using the pH scale instead of using the concentration of hydrogen ions.
5.00 g of an impure sample of hydrated ethanedioic acid, (COOH)2•2H2O, was dissolved in water to make 1.00 dm3 of solution. 25.0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated against a 0.100 mol dm-3 solution of sodium hydroxide using a suitable indicator.
(COOH)2 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) → (COONa)2 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
The mean value of the titre was 14.0 cm3.
(i) Calculate the amount, in mol, of NaOH in 14.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm-3 solution.
(ii) Calculate the amount, in mol, of ethanedioic acid in each 25.0 cm3 sample.
(iii) Determine the percentage purity of the hydrated ethanedioic acid sample.
The Lewis (electron dot) structure of the ethanedioate ion is shown below.
Outline why all the C–O bond lengths in the ethanedioate ion are the same length and suggest a value for them. Use section 10 of the data booklet.
Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O, causes depletion of ozone in the stratosphere.
Different sources of N2O have different ratios of 14N:15N.
Outline why ozone in the stratosphere is important.
State one analytical technique that could be used to determine the ratio of 14N:15N.
A sample of gas was enriched to contain 2 % by mass of 15N with the remainder being 14N.
Calculate the relative molecular mass of the resulting N2O.
Predict, giving two reasons, how the first ionization energy of 15N compares with that of 14N.
Suggest why it is surprising that dinitrogen monoxide dissolves in water to give a neutral solution.
Copper forms two chlorides, copper(I) chloride and copper(II) chloride.
An electrolysis cell was assembled using graphite electrodes and connected as shown.
State the electron configuration of the Cu+ ion.
Copper(II) chloride is used as a catalyst in the production of chlorine from hydrogen chloride.
4HCl (g) + O2 (g) → 2Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHθ, in kJ, for this reaction, using section 12 of the data booklet.
The diagram shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution and potential energy profile for the reaction without a catalyst.
Annotate both charts to show the activation energy for the catalysed reaction, using the label Ea (cat).
Explain how the catalyst increases the rate of the reaction.
Solid copper(II) chloride absorbs moisture from the atmosphere to form a hydrate of formula CuCl2•H2O.
A student heated a sample of hydrated copper(II) chloride, in order to determine the value of . The following results were obtained:
Mass of crucible = 16.221 g
Initial mass of crucible and hydrated copper(II) chloride = 18.360 g
Final mass of crucible and anhydrous copper(II) chloride = 17.917 g
Determine the value of .
State how current is conducted through the wires and through the electrolyte.
Wires:
Electrolyte:
Write the half-equation for the formation of gas bubbles at electrode 1.
This question is about peroxides.
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes to water and oxygen when a catalyst such as potassium iodide, KI, is added.
2H2O2 (aq) O2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Suggest why many chemicals, including hydrogen peroxide, are kept in brown bottles instead of clear colourless bottles.
In a laboratory experiment solutions of potassium iodide and hydrogen peroxide were mixed and the volume of oxygen generated was recorded. The volume was adjusted to 0 at t = 0.
The data for the first trial is given below.
Plot a graph on the axes below and from it determine the average rate of formation of oxygen gas in cm3 O2 (g) s−1.
Average rate of reaction:
Additional experiments were carried out at an elevated temperature. On the axes below, sketch Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves at two temperatures T1 and T2, where T2 > T1.
Apart from a greater frequency of collisions, explain, by annotating your graphs in (b)(ii), why an increased temperature causes the rate of reaction to increase.
MnO2 is another possible catalyst for the reaction. State the IUPAC name for MnO2.
Comment on why peracetic acid, CH3COOOH, is always sold in solution with ethanoic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
H2O2 (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) CH3COOOH (aq) + H2O (l)
Sodium percarbonate, 2Na2CO3•3H2O2, is an adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide and is used as a cleaning agent.
Mr (2Na2CO3•3H2O2) = 314.04
Calculate the percentage by mass of hydrogen peroxide in sodium percarbonate, giving your answer to two decimal places.
There are many oxides of silver with the formula AgxOy. All of them decompose into their elements when heated strongly.
After heating 3.760 g of a silver oxide 3.275 g of silver remained. Determine the empirical formula of AgxOy.
Suggest why the final mass of solid obtained by heating 3.760 g of AgxOy may be greater than 3.275 g giving one design improvement for your proposed suggestion. Ignore any possible errors in the weighing procedure.
Naturally occurring silver is composed of two stable isotopes, 107Ag and 109Ag.
The relative atomic mass of silver is 107.87. Show that isotope 107Ag is more abundant.
Some oxides of period 3, such as Na2O and P4O10, react with water. A spatula measure of each oxide was added to a separate 100 cm3 flask containing distilled water and a few drops of bromothymol blue indicator.
The indicator is listed in section 22 of the data booklet.
Deduce the colour of the resulting solution and the chemical formula of the product formed after reaction with water for each oxide.
Explain the electrical conductivity of molten Na2O and P4O10.
Outline the model of electron configuration deduced from the hydrogen line emission spectrum (Bohr’s model).
Carbonated water is produced when carbon dioxide is dissolved in water under pressure.
The following equilibria are established.
Carbon dioxide acts as a weak acid.
Soda water has sodium hydrogencarbonate, NaHCO3, dissolved in the carbonated water.
Distinguish between a weak and strong acid.
Weak acid:
Strong acid:
The hydrogencarbonate ion, produced in Equilibrium (2), can also act as an acid.
State the formula of its conjugate base.
When a bottle of carbonated water is opened, these equilibria are disturbed.
State, giving a reason, how a decrease in pressure affects the position of Equilibrium (1).
Predict, referring to Equilibrium (2), how the added sodium hydrogencarbonate affects the pH.(Assume pressure and temperature remain constant.)
100.0 cm3 of soda water contains 3.0 × 10−2 g NaHCO3.
Calculate the concentration of NaHCO3 in mol dm−3.
Identify the type of bonding in sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Between sodium and hydrogencarbonate:
Between hydrogen and oxygen in hydrogencarbonate:
A student titrated an ethanoic acid solution, CH3COOH (aq), against 50.0 cm3 of 0.995 mol dm–3 sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq), to determine its concentration.
The temperature of the reaction mixture was measured after each acid addition and plotted against the volume of acid.
Curves X and Y were obtained when a metal carbonate reacted with the same volume of ethanoic acid under two different conditions.
Using the graph, estimate the initial temperature of the solution.
Determine the maximum temperature reached in the experiment by analysing the graph.
Calculate the concentration of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, in mol dm–3.
Determine the heat change, q, in kJ, for the neutralization reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide.
Assume the specific heat capacities of the solutions and their densities are those of water.
Calculate the enthalpy change, ΔH, in kJ mol–1, for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide.
Explain the shape of curve X in terms of the collision theory.
Suggest one possible reason for the differences between curves X and Y.
Ammonia, NH3, is industrially important for the manufacture of fertilizers, explosives and plastics.
Ammonia is produced by the Haber–Bosch process which involves the equilibrium:
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g)
The effect of temperature on the position of equilibrium depends on the enthalpy change of the reaction.
Ammonia is soluble in water and forms an alkaline solution:
NH3 (g) + H2O (l) NH4+ (aq) + HO– (aq)
Draw arrows in the boxes to represent the electron configuration of a nitrogen atom.
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structure of the ammonia molecule.
Deduce the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kc, for this equation.
Explain why an increase in pressure shifts the position of equilibrium towards the products and how this affects the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc.
State how the use of a catalyst affects the position of the equilibrium.
Determine the enthalpy change, ΔH, for the Haber–Bosch process, in kJ. Use Section 11 of the data booklet.
Calculate the enthalpy change, ΔH⦵, for the Haber–Bosch process, in kJ, using the following data.
.
Suggest why the values obtained in (d)(i) and (d)(ii) differ.
State the relationship between NH4+ and NH3 in terms of the Brønsted–Lowry theory.
Determine the concentration, in mol dm–3, of the solution formed when 900.0 dm3 of NH3 (g) at 300.0 K and 100.0 kPa, is dissolved in water to form 2.00 dm3 of solution. Use sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
Calculate the concentration of hydroxide ions in an ammonia solution with pH = 9.3. Use sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
Vanadium, another transition metal, has a number of different oxidation states.
Determine the oxidation state of vanadium in each of the following species.
Formulate an equation for the reaction between VO2+(aq) and V2+(aq) in acidic solution to form V3+(aq).
This question is about carbon and chlorine compounds.
Ethane, C2H6, reacts with chlorine in sunlight. State the type of this reaction and the name of the mechanism by which it occurs.
Formulate equations for the two propagation steps and one termination step in the formation of chloroethane from ethane.
One possible product, X, of the reaction of ethane with chlorine has the following composition by mass:
carbon: 24.27%, hydrogen: 4.08%, chlorine: 71.65%
Determine the empirical formula of the product.
The mass and 1HNMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its structural formula and hence the name of the compound.
Chloroethene, C2H3Cl, can undergo polymerization. Draw a section of the polymer with three repeating units.